Pineal Gland - Your Third Eye?
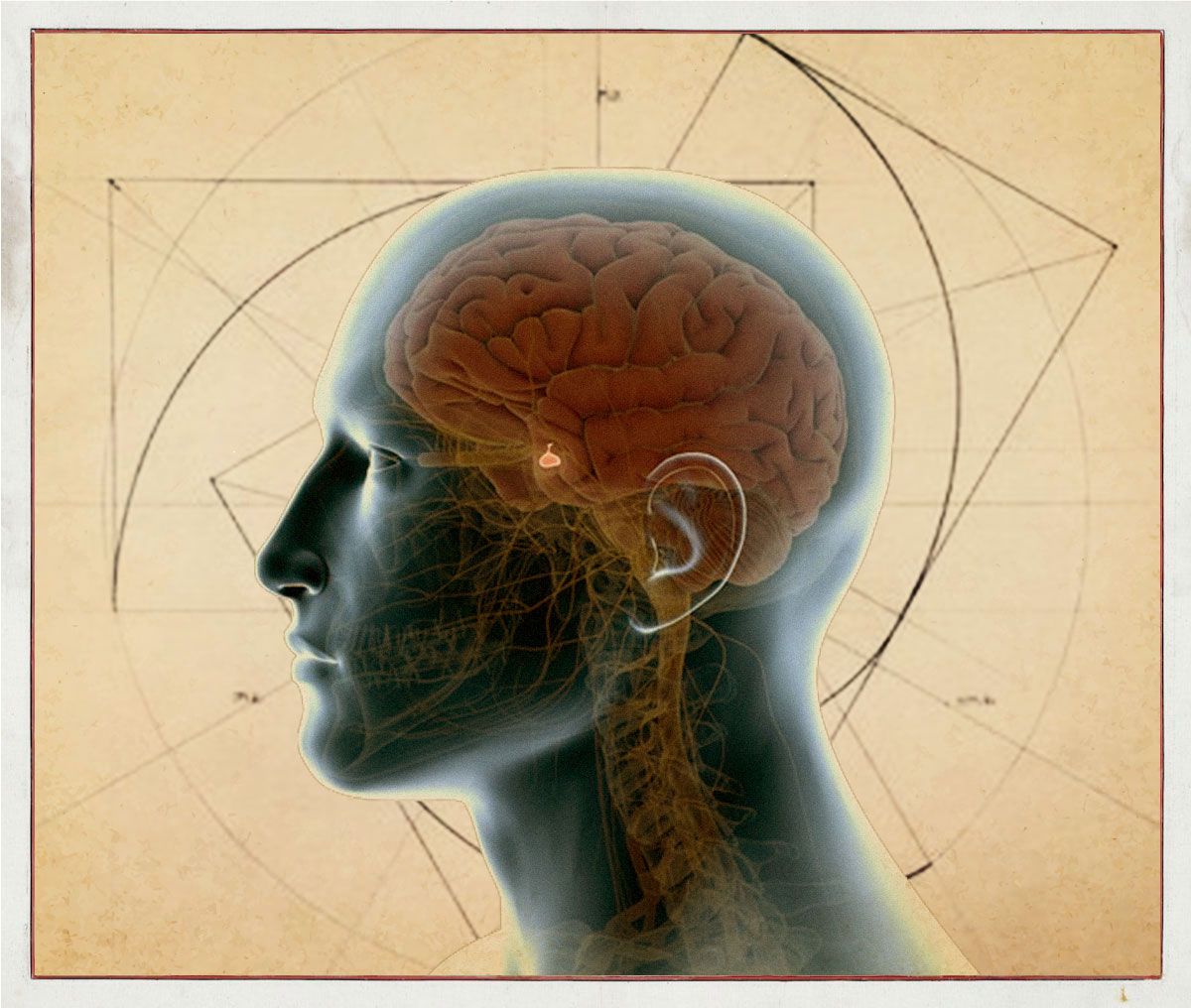
The pineal gland, a small endocrine organ nestled deep within the brain, has long captivated scientists and spiritual thinkers alike due to its mysterious nature and potential influence on human physiology and consciousness. While its exact functions are still being unravelled, recent scientific advancements have shed light on its role in regulating various physiological processes as well as the factors that can impact its functioning. This article delves into the intricate world of the pineal gland, explores the elements that can affect its operation, and examines how lifestyle choices can either enhance or compromise its functionality.
The Pineal Gland: A Glimpse into its Role
Situated in the central part of the brain, the pineal gland plays a pivotal role in the body's endocrine system. One of its most recognised functions is the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle through the secretion of melatonin. This hormone, often referred to as the "hormone of darkness," is synthesised and released by the pineal gland in response to decreasing levels of light. Melatonin helps synchronise the body's internal clock, or circadian rhythm, with the day-night cycle, aiding in the initiation and maintenance of sleep.
The pineal gland's role extends beyond melatonin production. It is also involved in regulating various physiological processes, including reproductive function, immune response, and mood regulation. Studies have indicated that the pineal gland's influence on reproductive function is partly mediated through its interaction with the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Additionally, research suggests that the pineal gland might play a role in modulating the body's immune response by influencing the production of immune-related molecules.
Factors Influencing Pineal Gland Functioning
Several factors can influence the functioning of the pineal gland, potentially impacting its ability to carry out its regulatory roles effectively. One significant factor is exposure to light. Artificial light sources, particularly those emitting blue light, can disrupt the natural production of melatonin by suppressing its secretion. This disruption can lead to disturbances in sleep patterns and circadian rhythms, contributing to sleep disorders and other health issues.
Environmental pollutants also pose a threat to pineal gland function. Fluoride, for instance, has been shown to accumulate in the pineal gland and could potentially affect melatonin synthesis. Some studies suggest that excessive fluoride exposure might impair pineal gland function, potentially disrupting sleep and circadian rhythms. Additionally, exposure to certain heavy metals and chemicals has been linked to pineal gland calcification, which could impact its overall function.
Lifestyle Impacts: Positive and Negative
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in influencing the health and functioning of the pineal gland. Let's delve into both the positive and negative impacts that lifestyle factors can have on this enigmatic organ.
Positive Lifestyle Impacts:
- Sunlight Exposure: Natural sunlight exposure during the day is essential for maintaining a healthy circadian rhythm. Spending time outdoors in the morning can help synchronise the body's internal clock and improve sleep quality.
- Darkness at Night: Creating a dark sleeping environment promotes optimal melatonin production. Minimising exposure to artificial light sources, especially screens emitting blue light, before bedtime can help support the pineal gland's function.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall endocrine health, including the pineal gland. Antioxidants protect the pineal gland from oxidative stress, potentially preserving its function.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise has been shown to positively influence sleep quality and circadian rhythms. Engaging in physical activity during the day can enhance the body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
Negative Lifestyle Impacts:
- Artificial Light: Excessive exposure to artificial light, especially in the evening, can disrupt melatonin secretion and disrupt the circadian rhythm. Limiting screen time before bedtime and using dim lighting in the evening can mitigate this effect.
- Unhealthy Sleep Habits: Inconsistent sleep schedules and inadequate sleep can negatively impact the pineal gland's function. Chronic sleep deprivation can disrupt the body's hormonal balance and impair overall health.
- Stress and cortisol: Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can disrupt pineal gland function and melatonin production. Practicing stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and meditation, can support pineal health.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming an excessive amount of processed foods, high in sugar and additives, could potentially impact pineal gland function. Additionally, some research suggests that a high-fluoride diet might affect the pineal gland.
In conclusion, the pineal gland, often dubbed the "third eye," plays a multifaceted role in regulating various physiological processes within the body. From orchestrating the sleep-wake cycle to potentially influencing reproductive function and immune response, this enigmatic organ's functions continue to captivate researchers and medical professionals. However, factors such as light exposure, environmental pollutants, and lifestyle choices can significantly impact its functioning.
By adopting a mindful approach to lifestyle choices, individuals can positively influence the health of their pineal gland. Prioritising healthy sleep habits, managing stress, and making informed dietary choices can contribute to optimal pineal gland function and overall well-being. As scientific knowledge continues to advance, unravelling the complexities of the pineal gland's role in human health will undoubtedly shed further light on its significance in our lives.